Sections
Overview
AdSense Review
Overall Rating

Why Publishers Like It
It is generally seen as the gold standard of contextual ad programs. Google owns about a third of the global online ad market & has a higher share in some locations (especially outside of the US, China & South Korea) as well as some categories like mobile & search ads.
When it works, it can be a terrific set-n-forget revenue source which helps subsidize the creation of additional online content. A number of great features are
- industry leading payouts (due to the depth of their ad network)
- combining contextual, display, site targeting & ad retargeting in a single offering
- the ability to tie it in with Google Analytics (to give granular page-level performance data)
- the ability to serve ads using DoubleClick for Publishers (which allows features like also selling direct ads & setting links to open in a new window)
One of the other features which was fantastic was the ability to tie click performance back to keyword data. That is still somewhat possible, however Google currently hides keyword data on about 90% of organic search traffic and Yahoo! hides keyword data on about 50% of search traffic, so the ability to "close the loop" on the keyword level performance data is not as strong as it once was.
Growing Success With Partners
The success of AdSense has led to the founding of multiple ad yield optimization startups like AdPushup and Ezioc. Companies like them test different ad layouts, ad colors and placement locations, sharing much of the incremental ad yield with publishers.
Why People Dislike It - Poor Communications & Bans
A limited amount of competition over the years has caused them to be aggressive & adversarial toward many of their partners. For years they refused to disclose ad revenue share & they only disclosed it in 2010 after a lawsuit in Italy forced them to. At one point Larry Page even stated he thought the concept of customer support is ridiculous.
There have been numerous cases where longstanding accounts were banned out of the blue without warning - with the most recent earning period clawed back.
Some individuals have complained to regulators or taken them to court over the practice, however such a fight can be expensive & time consuming, and success is not guaranteed. More recently there has been an alleged employee leak, reports of accounts being closed right before publisher payouts are due, and a class action lawsuit.
 Even outside of account bans, some publishers still face significant margin risk as Google's priorities change. Demand Media's eHow is indeed a cautionary tale.
Even outside of account bans, some publishers still face significant margin risk as Google's priorities change. Demand Media's eHow is indeed a cautionary tale.
As Google reshapes the web in its own image, on highly commercial keywords it publishes search result pages which are almost entirely ads or "knowledge graph" listings with ads above the fold. And then they roll out algorithms which penalize publishers for being too "ad heavy." Yet if you look at their heat map, the "best practices" almost seem like a recipe for trouble. And old case studies from publishers long since penalized have been removed.
Their program can seem rock solid while it is working, but the level of churn is quite high. In this article Susan Wojcicki mentioned Google has "some 2 million sites" in their display network. In a 2012 blog post they published the following graph, highlighting how they had disabled ad serving to about 1.5 million sites in the 4 years prior.
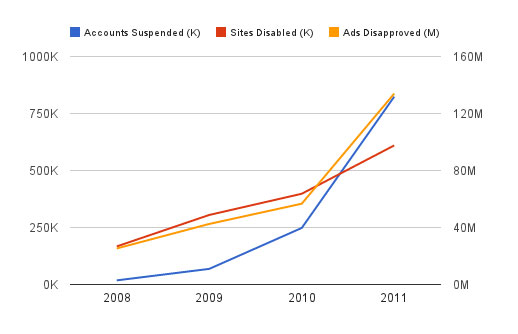
In early 2014 they followed up that post with another one, highlighting the following stats for 2013:
we had blacklisted more than 200,000 total publisher pages, an encouraging decline from last year, and disapproved more than 3,000,000 attempts to join our AdSense network. We also removed more than 250,000 publisher accounts for various policy violations.
If each publisher has an average of 1 website, that would indicate something like a 12.5% of publishers faced banning in 2013. If each publisher has an average of 2 sites, it would mean they banned 25% of their partners in a single year - and these bans are lifetime bans.
Consider how they banned AdBlock Plus from their Play Store, only to later allow it once Google search ads were re-enabled in the plugin, yet AdSense ads on publisher sites remained blocked by the plugin.
>>> Sign up to activate your AdSense publisher account today.
Multiple other partners work to syndicate Google ads without requiring the publisher have a direct relationship with Google. Perhaps the most popular among these are Ezioc & adpushup. Others would include services like Clickio & The Moneytizer. I unfortunately haven't had the time to test out all these sorts of third party ad mediation services, but in some cases it could certainly make sense to test them if you had trouble opening an AdSense account or wanted to not have all your ad revenue tied to a single network that might scrub over 10% of their partners in any given year.
Onto the top competing contextual ad networks...
Media.net

Overall Rating

Exciting offer...
Bonus Earnings Offer
We partnered with Media.net to offer you a 10% earning bonus for your first 3 months in their program. When you click this link and sign up today, Media.net will add an extra 10%.
General Review
Many smaller networks which are AdSense competitors have a huge fall off, to where if you earned 50 cents or a dollar a click with AdSense, you'd see penny and nickle clicks. Thankfully Media.net is nothing like that & they are perhaps the best at competing on a eCPM basis. Their interface is quite easy to use, both in terms of creating & customizing new ad units and in tracking performance reports.
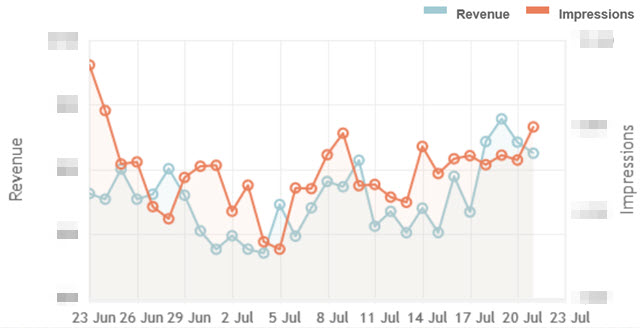
In most markets Media.net won't vastly outperform AdSense, but it is certainly worth testing & may do far better than one would expect, particularly in light of how weak the Yahoo! Publisher Network performed many years ago. I've read some Media.net reviews which were a bit negative, but many of those were from people earning under $1 a day or such. Since Media.net lacks Google's advertising network depth & scale, they try to offset that with better ad integration using a manually intensive work process to really help the ads match the look and feel of your sites. It is worth noting that unless you have a decent amount of scale they probably won't be able to justify spending a lot of resources working on custom ad integration for your website.
Competition shifts the balance of power. When companies feel like they don't have to compete they can start believing things like "the whole concept of customer support is absurd." Even if using Media.net were revenue neutral, it would still be worth doing in order to help shift that balance of power in favor of publishers. Some other large web players like Mozilla Firefox have certainly indicated they understand the importance of that sort of competition.
A Successful Exit
Media.net was so successful they were acquired for $900 million, even while Yahoo! itself sold for only $4.8 billion. The success of Media.net has led to other companies like Inuvo trying to build similar offerings. System1 (formerly OpenMail) acquired InfoSpace for $45 million and has access to the Bing and Google ad feeds, but Media.net still remains the unmatched #1 competitor to Google AdSense.
Bonus Earnings Offer
We partnered with Media.net to offer you a 10% earning bonus for your first 3 months in their program. When you click this link and sign up today, Media.net will add an extra 10%.
Great Features
- Competitive eCPM when compared against AdSense in many categories.
- Particularly strong ad performance on mobile devices.
- Can be used in conjunction with AdSense.
- Has some standard ad unit sizes & some that are custom, which gives you flexibility in terms of integrating them in typical ad spots and in terms of having units which look different than common ones and thus have greater eye appeal than a standard 468x60 or 728x90 banner.
- Leverages the Yahoo! Bing Network, which gives it a fairly decent advertiser base & network scale to tap into to ensure there are relevant ads for most topics. I believe one thing that has helped them do so well is Microsoft has done a much better job on pricing click quality than many networks did in years past.
- Since they are not a monopoly, Media.net believes in the concept of customer service & their partner communications are much clearer. You don't have to pull down millions of dollars a year to be considered a valued partner.
- Their customer support team not only communicates clearly with publishers, but also works to help improve ad integration. Support is perhaps one of their best attributes.
- Once your account has been established and they see strong traffic quality they are generally quite quick at approving any additional sites you add to your account.
- In addition to offering contextual ads, Media.net has a partnership to serve Google display ads (though publishers have to be invited to have those features enabled).
- While earning statistics are not real-time, they provide them the following day.
- Fast Net-30 payouts.
Drawbacks
The main drawbacks would be:
- They require English as your primary language & that your site receives the majority of its traffic from the United States, Canada, and the United Kingdom. If you operate outside those markets, then they wouldn't be a great fit at the moment (though who knows where they may be in a couple years as Bing gets more aggressive with international expansion). The acquisition by a Chinese company promises to accelerate international growth (particularly in China) and drive further ad expansion in video and other formats.
- It can take a while to get a new account approved, so it is worth applying early to have some experience and to have a backup in place in case anything should happen to your AdSense account.
- Inability to split test units (though if you are doing enough volume your customer support person will help set up and implement a split test for you).
- While they do offer statistics on a per-site, per-day & per-ad unit basis (along with pageview stats), they currently do not offer data down to the page or keyword level. They provide data on earnings, pageviews & eCPM; but they currently do not provide click or CPC data. (I believe they will be adding more granular metrics fairly soon).
- With Yahoo! getting acquired by Verizon & Media.net getting acquired by a Chinese company, it remains to be seen if Media.net will enjoy the same revenue share with upstream ad partners & if they will be able to keep passing on such a high revenue share to partners using their network.
>>> Sign up to activate your Media.net publisher account today.
Amazon Associates

Overall Rating

Amazon enjoys an amazing share of ecommerce sales and they are growing their share of market over time. Their broad selection means that if something is for sale online there is a good chance they have it listed on their site, and there is a good chance users already have an account registered with them, so that boosts conversion rates on desktop and mobile devices. They are to ecommerce as Google is to search and Facebook is to social.
Their affiliate program comes via tiered structure, where the more items you sell each month the higher a revenue share they offer. Their tiers and guidelines may change over time, but here is a chart as of September 2016 to highlight the general approach.
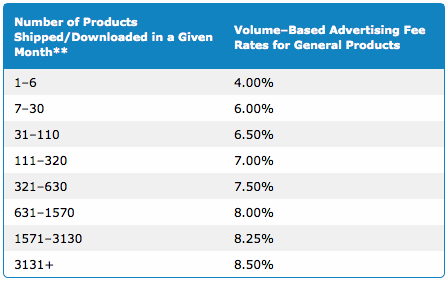
Select categories like computers may have a lower revenue share & a max capped commission per sale. They have also implemented some other rules to prevent gaming the system with free ebook downloads and other "purchases" of dubious commercial value. Click here to see more about Amazon's current category-based payments and volume tiers.
Amazon's affiliate cookie is quite short at only 24 hours, but this is somewhat offset by their high conversion rates & by many consumers who visit their site to buy x and also buy y and z while they are there.
Amazon launched Native Shopping Ads which can be automatically targeted using on-page content to drive relevancy, or webmasters can programmatically drive ad topics using a page's title or a different custom variable set up for ad targeting.
Amazon also moved into offering a retargeting display network for publishers, which leverages consumer browsing and shopping behavior on Amazon.com to improve ad relevancy.
Some sites are a good fit for AdSense & some sites are a good fit for affiliate programs. In some cases using them in combination can drive incremental revenues without cannibalizing existing revenue streams.
The more diverse your income pool is the less a risk of something going astray if any given partner shuts down or arbitrarily banning you.
Amazon has also quietly launched an ad network by invite. Mid-sized publishers can request access to their Unified Ad Marketplace, though it requires using Google's DFP for ad serving.
Facebook Audience Network

Overall Rating

Facebook believes they have strategically superior user information based on the usage of their mobile app. They have tried to extend their ad network out to the desktop web, but pulled back due to high prevalence of fraud. The Facebook Audience Network is thus primarily for monetizing mobile applications and mobile websites. They offer typical banner ads, interstitial ads & are experimenting with video ads.
There is a significant gap between what Facebook typically charges for ad clicks on their owned and operated sites versus what they charge for clicks on ads to partner sites. A few weeks ago a friend sent me the following example of a new campaign he set up to highlight how large this gap can be.
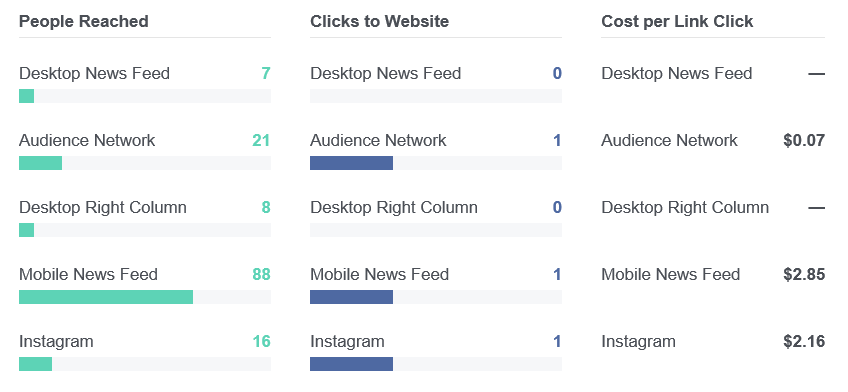
In the longer term, Facebook is more interested in pulling content into their website rather than spreading their ad network outward. This ad network may be effective for monetizing mobile games, but for traditional websites the yields are not remarkably high. It is typically perhaps closer to something like an Outbrain rather than a Google AdSense or Media.net in terms of yield.
Chitika

Chitika Ad Network Shut Down
On April 17, 2019 Chitika
announced it was shutting down immediately. Back in 2010 when Yahoo! announced they were shutting down the Yahoo! Publisher Network
they recommended publishers shift to using Chitika. The network had a lot of exposure on many prominent blogs, so the abrupt closure of Chitika took many publishers by surprise.
Overall Rating

Chitika launched in 2003 and made waves with their eMiniMalls back in 2005. Darren Rowse helped put them on the map when he reviewed them after seeing great performance on his photography website. As a smaller independent third party service they kept innovating by cleverly used signals like search keyword to help drive ad targeting on the landing page. Of course after Google defaulted to keyword (not provided) on organic search Chitika had to lean harder into a variety of other signals - like file names.
That Chitika is around over a decade after launching is a testament to their fortitude and fighting spirit, as many providers which launched after them have already been shut down. AdBrite was created the year before Chitika and shut down on February 1, 2013. Yahoo! launched their own program (named the Yahoo! Publisher Network) on August 2, 2005 but announced its closure on March 31, 2010. When they closed down they recommended publishers use Chitika.
Great Features
- Account approval is quite fast. You can add the ad code to new sites quickly after your account is approved.
- Offers a variety of ad formats including contextual ads, ad links, inline text ads, and a footer bar option.
- Daily stat updates on clicks, CPC, earnings, pageviews & eCPMs.
- Fast payouts.
Drawbacks
- When doing side by side tests we've generally seen lower earnings from Chitika than Media.net or Google AdSense. If your site is about a fairly low commercial interest topic where click prices are fairly low across the board then Chitika can be decently competitive, but if your sites cover topics where clicks often go for multiple dollars there tends to be a more significant fall off.
- While Chitikia automatically approves new accounts, I believe the initial ad feed they offer might be a more basic one with lower earnings potential. Sometimes you have to wait a few days in order for your CPC to really ramp up.
Join Today
>>> Sign up to activate your Chitika publisher account today.
Yahoo! Publisher Network

CLOSED
Yahoo! launched their own contextual ad program (named the Yahoo! Publisher Network) on August 2, 2005 but announced its closure on March 31, 2010. When they closed down they recommended publishers use Chitika. Yahoo! ultimately had a couple problems which prevented them from competing:
- their ads were primarily driven by max CPC rather than relevancy matching, which caused many publishers to complain about Vonange ads everywhere
- they did not use smart pricing to optimize ad click costs as well as Google did
- their ad network was not quite as deep
The third of the above 3 wouldn't have mattered so much if the first issue wasn't so overt.
After shutting down in 2010, Yahoo! announced they inked a long-term agreement with Media.net on September 27, 2012 to run a contextual ad program (which was reviewed above). In 2013 Yahoo! also signed a non-exclusive deal with Google to syndicate AdSense and mobile AdMob ads.
Microsoft pubCenter

Overall Rating

Microsoft has an ad program named pubCenter. However they only briefly had it open to smaller independent webmasters before shifting it toward focusing primarily on mobile ads and Windows 8 apps. When it first opened up via a YieldBuild partnership it performed strongly, but then they used smart pricing to drive down ad rates.
If you are not developing mobile apps for Windows phones & Windows 8 apps you are probably better off working with Media.net to leverage Bing's network.
In-Text Ad Networks: Infolinks vs Kontera vs Vibrant Media Intellitxt



Overall Rating

We have tested all of these to some degree, but have never seen a huge lift from them when compared against the above mentioned programs.
In many cases the "in-text" ad networks promote themselves as offering free incremental revenues, however if a site's user experience is worse & users click the back button quicker that can not only impact the pageviews of the visitor (as someone who clicks back doesn't view a second page), but those sorts of negative engagement metrics can also fold into algorithms like Google's Panda, which can cause the site to ranked lower in the search results.
And if that were not bad enough, Google is looking down upon these types of ads in their manual review process as well. The March 31, 2014 leaked version of Google's remote rater guidelines state:
- "Ads and should be arranged so as not to distract from the MC—Ads and SC are there should the user want them, but they should be easily “ignorable” if the user is not interested."
- "It should be clear what parts of the page are Ads, either by explicit labeling or simply by page organization or design."
- "Many Ads or highly distracting Ads on the visible part of the page when it first loads in the browser (before you do any scrolling), making it difficult to read the MC."
- "the popover ads (the words that are double underlined in blue) can make the main content difficult to read, resulting in a poor user experience."
In the above, the MC stands for [main content] and SC stands for [supplemental content]. What they are saying there is that ads blended into the main content can create a poor user experience and thus be justification for giving the site a poor rating. If enough remote raters flag a site as being a poor user experience, that could flag it for review & have engineers penalize the site with a manual penalty.
The above "engagement" sort of issues related to the Panda algorithm are also why I generally don't like pop ups or aggressive overlays like Undertone or similar on smaller niche sites. I'm even hesitant to use something like Adiply, let alone something as aggressive as Exit Junction.
These in-text ads are becoming more widespread. Viglink and Skimlinks are automated affiliate monetization solutions for those who do not want to have to sign up with numerous sites and networks. BrandCrumb is a similar solution which has select brands registered. LinkSmart is yet another in-text ad network.
The above were some of the better known contextual providers, but there are are a variety of other ad formats to monetize sites with, including: display, content recommendation, video, mobile and affiliate marketing. We review some of the other options below.
Other Affiliate Networks
- The eBay Partner Network is great for sites which promote vintage goods & collectibles.
- CJ affiliate by Conversant is the new name for Commission Junction, which has long been the #1 online affiliate network.
- Rakuten LinkShare has for years fought CJ for the leadership position in the affiliate network space.
- ShareASale is a growing affiliate network which has been growing their share in the market for years.
- Viglink and Skimlinks are automated affiliate monetization solutions for those who do not want to have to sign up with numerous sites and networks. BrandCrumb is a similar solution which has select brands registered.
- Clickbank is a leading marketplace for digital downloads. They skew heavy toward the "get rich quick" niche, but if you get out of the biz op are some of their products might be decent. Since they sell high margin digital products the typical affiliate commission is a far higher percent than merchants selling physical goods.
- MyCommerce - a more upscale Clickbank-like digital maketplace by Digital River, which skews primarily toward software.
Display Ads & Self-serve Providers
There are many types of networks and options for display.
- Ad servers / self-serve sales: there are dozens of options for self-served display. To highlight a few: DoubleClick for Publisher, OpenX, AdJuggler, IndustryBrains & BuySellAds. Some of them have a variety of ways to differentiate their offerings, like DoubleClick for Publisher backfills with AdSense and BuySellAds has easy on-site signup options and helps pitch some of their publishers to advertisers. Publishers selling directly can of course also differentiate their offerings from the generic offerings by surveying their audience and offering custom sponsorship integration opportunities.
- Display ads: once again, there are many. To highlight a few: TribalFusion, Sovrn, PulsePoint, Rubicon Project, Vertoz, Advertising.com, Adblade.com, Adknowledge, Conversant Media, Bidvertiser, & Casale Media.
- Video networks: once again there are numerous options including: YouTube Partner Program, Adap.tv, BrightRoll, Tremor Video, Videology, SpotXChange, LiveRail, Adobe Auditute, Microsoft Advertising & YuMe.
- Mobile: there are many mobile & app ad options including: Google's AdMob, Apple iAd, Airpush, Facebook Audience Network, Twitter's MoPub, Microsoft pubCenter & Amazon mobile ad network
Content Recommendation
These appear on various mainstream media sites as "also in the news" or "from around the web" or similar. Here is an example:
Last Updated: April 26, 2019.


