A while ago I wrote a bit about TrustRank after reading the PDF about it.
It is fairly easy to understand many of the concepts of it (like attenuating a possitive trust score or offsetting the effects of link spam with a negative trust score), but it is even easier to understand them if you visualize the concept of trust attenuation.
Most sites are not exceptionally compelling, so there are usually not many legitimate hubs in any industry, but many sites are glorified link farms which will not pass any positive trust value.
For a while I helped promote many directories, but many of the new ones on the market have little to no legitimate value, and some of the links from them may even have negative value.
I just wrote an article called TrustRank & the Company You Keep, in which I made this graphic explaining the concept of AntiTrust (yet another SEO phrase I made up hehehe).
The red X's represent things that should be, but are not there.
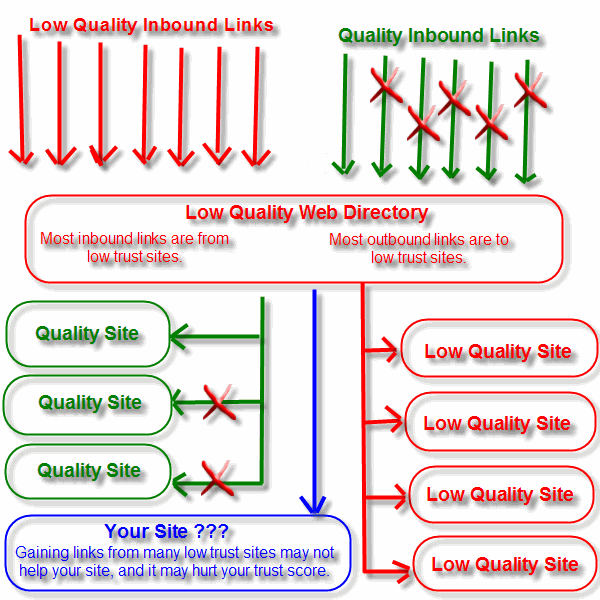
Yes, I know, the drop shadow is too dark, my web designer friend already yelled at me for that. Other than that, I hope the image clearly demonstrates the concept I was trying to get across.
Other than drop shadow remarks, please leave comments on the article and image below.


