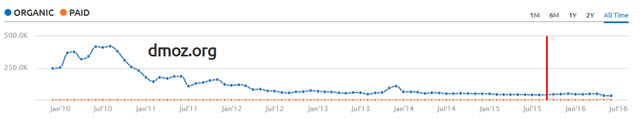
Last August I wrote a blog post about how attention merchants were sucking the value out of online publishing. In it I noted how the Yahoo! Directory disappeared & how even DMOZ saw a sharp drop in traffic & rankings over the past few years.
The concept of a neutral web is dead. In its place is agenda-driven media.
- Politically charged misinformed snippets.
- Ads cloaked as content.
- Public relations propaganda.
- Mostly correct (but politically insensitive) articles being "fact checked" where a minor detail is disputed to label the entire piece as not credible.
As the tech oligarchs broadly defund publishing, the publishers still need to eat. Aggregate information quality declines to make the numbers work. Companies which see their ad revenues slide 20%, 30% or 40% year after year can't justify maintaining the labor-intensive yet unmonetized side projects.
There is Wikipedia, but it is not without bias & beyond the value expressed in the hidden bias most of the remaining value from it flows on through to the attention merchant / audience aggregation / content scraper platforms.
Last month DMOZ announced they were closing on March 14th without much fanfare. And on March 17th the directory went offline.
A number of people have pushed to preserve & archive the DMOZ data. Some existing DMOZ editors are planning on launching a new directory under a different name but as of the 17th DMOZ editors put up a copy at dmoztools.net. Jim Boykin scraped DMOZ & uploaded a copy here. A couple other versions of DMOZ have been published at OpenDirectoryProject.org & Freemoz.org.
DMOZ was not without criticism or controversy,
Although site policies suggest that an individual site should be submitted to only one category, as of October 2007, Topix.com, a news aggregation site operated by DMOZ founder Rich Skrenta, has more than 17,000 listings.
Early in the history of DMOZ, its staff gave representatives of selected companies, such as Rolling Stone or CNN, editing access in order to list individual pages from their websites. Links to individual CNN articles were added until 2004, but were entirely removed from the directory in January 2008 due to the content being outdated and not considered worth the effort to maintain.
but by-and-large it added value to the structure of the web.
As search has advanced (algorithmic evolution, economic power, influence over publishers, enhanced bundling of distribution & user tracking) general web directories haven't been able to keep pace. Ultimately the web is a web of links & pages rather than a web of sites. Many great sites span multiple categories. Every large quality site has some misinformation on it. Every well-known interactive site has some great user contributions & user generated spam on it. Search engines have better signals about what pages are important & which pages have maintained importance over time. As search engines have improved link filtering algorithms & better incorporated user tracking in rankings, broad-based manual web directories had no chance.
The web of pages vs web of sites concept can be easily observed in how some of the early successful content platforms have broken down their broad-based content portals into a variety of niche sites.
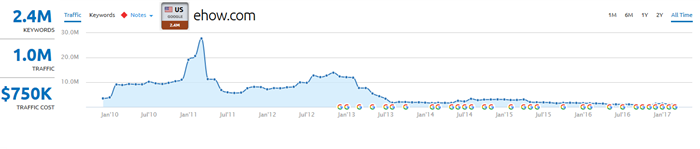
When links were (roughly) all that mattered, leveraging a website's link authority meant it was far more profitable for a large entity to keep publishing more content on the one main site. That is how eHow became the core of a multi-billion Dollar company.
Demand Media showed other publishers the way. And if the other existing sites were to stay competitive, they also had to water down content quality to make the numbers back out. The problem with this was the glut of content was lower ad rates. And the decline in ad rates was coupled with a shift away from a links-only view of search relevancy to a model based on weighting link profiles against user engagement metrics.
Websites with lots of links, lots of thin content & terrible engagement metrics were hit.
Kristen Moore, vp of marketing for Demand Media, explained what drove the most egregious aspects of eHow's editorial strategy: “There’s some not very bright people out there.”
eHow improved their site design, drastically reduced their ad density, removed millions of articles from their site, and waited. However nothing they did on that domain name was ever going to work. They dug too deep of a hole selling the growth story to pump a multi-billion Dollar valuation. And they generated so much animosity from journalists who felt overwork & underpaid that even when they did rank journalists would typically prefer to link to anything but them.
The flip side of that story is the newspaper chains, which rushed to partner with Demand Media to build eHow-inspired sections on their sites.
Brands which enjoy the Google brand subsidy are also quite hip to work with Demand Media, which breathes new life into once retired content: "Sometimes Demand will even dust off old content that’s been published but is no longer live and repurpose it for a brand."
As Facebook & Google grew more dominant in the online ad ecosystem they aggressively moved to suck in publisher content & shift advertiser spend onto their core properties. The rise of time spent on social sites only made it harder for websites to be sought out destination. Google also effectively cut off direct distribution by consolidating & de-monetizing the RSS reader space then shutting down a project they easily could have left run.
As the web got more competitive, bloggers & niche publications which were deeply specialized were able to steal marketshare in key verticals by leveraging a differentiated editorial opinion.
Even if they couldn't necessarily afford to build strong brands via advertising, they were worthy of a follow on some social media channels & perhaps an email subscription. And the best niche editorial remains worthy of a direct visit:
Everything about Techmeme and its lingering success seems to defy the contemporary wisdom of building a popular website. It publishes zero original reporting and is not a social network. It doesn’t have a mobile app or a newsletter or even much of a social presence beyond its Twitter account, which posts dry commodity news with zero flair for clickability.
As a work around to the Panda hits, sites like eHow are now becoming collections of niche-focused sites (Cuteness.com, Techwalla.com, Sapling.com, Leaf.tv, etc will join Livestrong.com & eHow.com). It appears to be working so far...
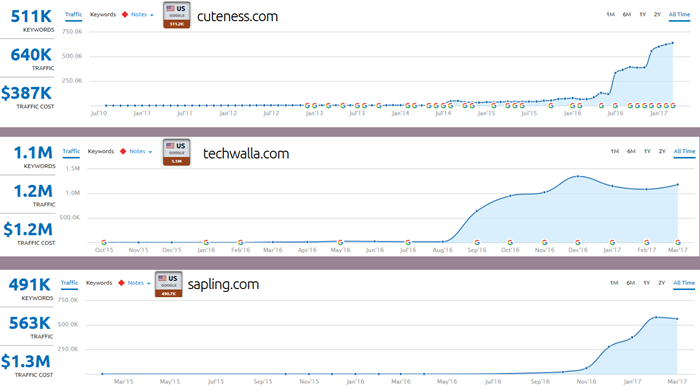
...but they may only be 1 Panda update away from finding out the new model isn't sustainable either.
About.com has done the same thing (TheSpruce.com, Verywell.com, Lifewire.com, TheBalance.com). Hundreds of millions of Dollars are riding on the hope that as the algorithms keep getting more granular they won't discover moving the content to niche brands wasn't enough.
As content moves around search engines with billions of Dollars in revenue can recalibrate rankings for each page & adjust rankings based on user experience. Did an influential "how to" guide become irrelevant after a software or hardware update? If so, they can see it didn't solve the user's problem and rank a more recent document which reflects the current software or hardware. Is a problem easy to solve with a short snippet of content? If so, that can get scraped into the search results.
Web directories which are built around sites rather than pages have no chance of competing against the billions of Dollars of monthly search ads & the full cycle user tracking search companies like Google & Bing can do with their integrated search engines, ad networks, web browsers & operating systems.
Arguably in most cases the idea of neutral-based publishing no longer works on the modern web. The shill gets exclusive stories. The political polemic gets automatic retweets from those who identify. The content which lacks agenda probably lacks the economics to pay for ads & buy distribution unless people can tell the creator loves what they do so much it influences them enough to repeatedly visit & perhaps pay for access.


