There are a lot of parallels between Google AdWords and SEO, and a lot of the beginner mistakes are the same for both traffic acquisition strategies. I figured it would be worth outlining some of the most common ones to help save you money on your search engine marketing campaigns.
- Weak Domain Name
- All Search Traffic Driven to Homepage
- No Link Building
- All Links to the Homepage
- No Link Anchor Text Variation
- No Focus on Quality
- Lacking On Page Optimization
- No Site Structure
- Site With No Value Add
- Competitive Saturated Market With Inadequate Budget
- Picking a Market for 1
- Pick a Market Which Does Not Monetize
- Over-Aggressive Monetization From Day 1
- What Other Common SEM Errors do You See?
1. Weak Domain Name
Google AdWords
When I interviewed Perry Marshall about AdWords he recommended split testing URLs because the URL can and does have a major impact on your ad clickthrough rate.
Since Google factors click-through rate (CTR) into their quality scores, anything that influences CTR influences your click prices. And while competitors can and will steal your AdWords ad copy, they CAN'T steal your domain name.
SEO
There are many potential errors that can be made with domain names. Two of the more common errors are creating a domain name that is impossible to remember and creating a name that restricts expansion.
Recommendations
Some people feel the need to limit their domain name budget to $10, but it is a foolish strategy. Almost every piece of marketing you do will be influenced by your domain name. Your domain name has limited recurring costs associated with it, but can represent a huge recurring market advantage or disadvantage. Yeah for CreditCards.com, and boo for cheapest-online-apply-credit-cards-and-loans.info.
- If you are using Google AdWords for a new product or a non-branded product then test clickthrough rates across multiple domain names.
- Make sure your domain name allows you to expand as needed. This is sorta an error I made early on with this site...I had no idea how successful the site would become when I started it and did not anticipate us creating the #1 SEO training program back when I thought of selling an ebook.
- Avoid names that are impossible to remember. If you intend to create something that is easy to market online and offline then your domain name must pass the phone test, which typically means avoiding hyphens & numbers. This is especially true if you are trying to build a big brand.
- If you feel your company may expand internationally it is best to buy any matching domain extensions where you might intend to eventually do business.
- Exact match domain names can create a big SEO advantage if you can afford them - since some engines may give them a relevancy boost and your domain name influences the anchor text people use when they link at your website.
2. All Search Traffic Driven to Homepage
Google AdWords
1 page can only be relevant for a certain sector of search queries. In an efficient market anyone who directs all traffic to the homepage will lose a lot of money.
Every additional click you force users to make has some amount of slippage. When using Google AdWords / pay per click marketing a small change in conversion rates can be the difference between sustained profits and sustained losses.
SEO
It is sorta impossible to make a page "optimized" for hundreds or thousands of popular keywords because eventually after you add enough different keywords in the page copy it ends up reading bad and it harms conversion rates.
With SEO efforts mis-directing traffic is not as obvious as it is with AdWords because you don't have to pay for every click. But giving users an irrelevant experience still means you are throwing money away and only operating at a fraction of your potential.
Recommendations
With the prevalence of Google (and web search in general) every page of your site is the front door. We navigate via search. So map out keywords against URLs and try to offer the most relevant user experience whenever possible.
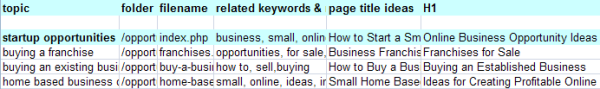
Observe how we map out core keywords, variations, and modifiers.
Some Google AdWords advertisers take perceived relevancy one step further and use the search query to help define the page content through the use of keyword insertion into their page copy and/or altering the page based on geographic information based on your computer's IP address.
3. No Link Building
Google AdWords
The equivalent of links to AdWords is keywords in your AdWords account. If you only advertise on 1 or 2 keywords you miss out on a large stream of relevant traffic.
SEO

If you build it they will come is simply not true in the search game. If it was easy to rank for competitive keywords without links then few companies would buy AdWords ads. You can't typically rank a new site until you have some level of awareness. Search engines follow people. Links are seen as votes of trust.
Recommendations
With AdWords, don't just bid on 1 keyword. Look for additional relevant variations that make sense. If you don't mind splashing out $50 you can also look at what competing sites are advertising on using SEM Rush, Keyword Spy, SpyFu, and/or KeyCompete. There are so many new tools popping up in this market segment that I have not had the time to review them all.
For SEO, download SEO for Firefox and the SEO Toolbar and look at how many links competing sites have and how many domain names those links come from. You will likely need to build some number of links in the range of what competing sites have (from a similar set of sites) to rank. Today is the perfect day to start building links. And yesterday was even better. ;)
4. All Links to the Homepage
Google AdWords
Since you are buying the links from the search engines based on keyword, this problem would be corrected by solving issue #2.
SEO
A variation of the above thinking. Most quality sites have useful content somewhere that people link to editorially. If all your links point at the homepage then that means you are not using anchor text from external links to boost your internal page ranks. In most markets that creates a big loss considering that some of those pages would get a lot of traffic with just a few more deep links which would yield higher rankings.
Recommendations
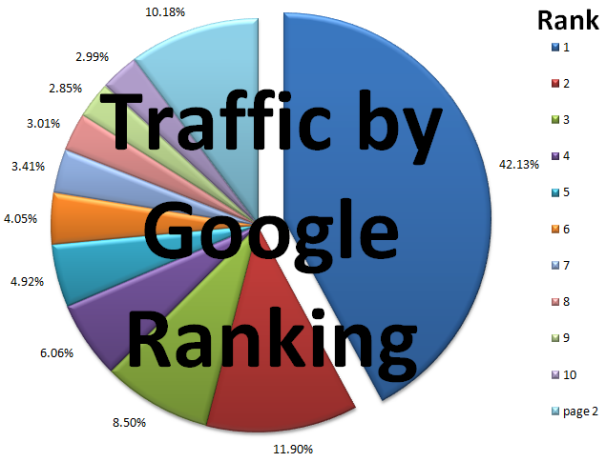
Search is a winner take most market. Analyze your traffic patterns, rankings, and target keywords to ensure you are promoting key pages. Look at top competing sites and keyword ranking values to gain additional insights.
Create linkworthy content that people would want to link at and push market it. The objective (vs self-interested) viewpoint here is "if you did not own your site what is unique about it that would make you want to visit it every week and/or recommend it to a friend?"
5. No Link Anchor Text Variation (or AdWords Ad Copy Variation)
Google AdWords
You shouldn't use the exact same ad copy on all of your keywords. You should segment it out by trying to understand user demand and create compelling advertising text that is relevant to the search query, relevant to the user demand, and relevant to your landing page. If you use a single generic boilerplate ad copy you are loosing a lot of money because your ad will not look as relevant as some of the top competing ads.
SEO
When people link to things naturally there tends to be some variation involved. If all your inbound links say "my keywords" then that can look suspicious...particularly if you are buying lots of links.
Recommendations
With AdWords, at a minimum you would want to use dynamic keyword insertion. But if you sell a lot of different products then you should try to find a way to match up small groups of relevant keywords against a set of ad copy. Make your core keywords stand out on their own, and be willing to be somewhat less descriptive with low search volume backfill keywords.
With SEO you should try to mix up your link anchor text when you are manually building links. If you create original compelling content that people want to link at (and push market it to the right audience) then that will also pull in natural anchor text.
6. No Focus on Quality
Google AdWords
Some advertisers are compelled to go after "cheap" clicks. But some of the more expensive keywords are expensive because they are associated with significant and valuable consumer demand.
SEO
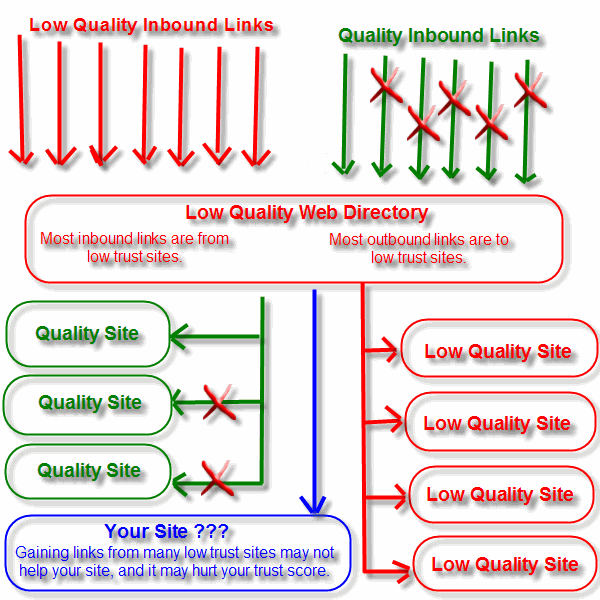
Google algorithms estimate the probability of a new site being quality or low quality. If you start off with 2,000+ "free" directory links you align your site with sites that are often of lower quality. Similarly, if you try to promote watered down or average content then few people will be receptive to those efforts.
Recommendations
There is nothing wrong with buying cheap traffic, but make sure you track the business value you get from that traffic. If you buy "cheap" traffic from 3rd tier ad networks and/or keywords without any commercial intent those will not build your business anywhere near as well as developing a solid traffic stream from valuable industry keywords on leading search engines.
Start your link building efforts with quality links first. As your site gets more trusted you can fill in some lower quality links as well, but you don't want to do it first, and you don't want to do it in bulk.
When you decide to do push marketing for link building make sure the content you are promoting is unique, original, useful, compelling, & citation-worthy.
7. Lacking On Page Optimization
Google AdWords
Quality user experience and usability are crucial to converting well. When users come from search to your site they are switching channels. The more cues you can give them that they are in the right place (like relevant page headings + navigation) the higher your conversion rates and visitor value should be.
SEO
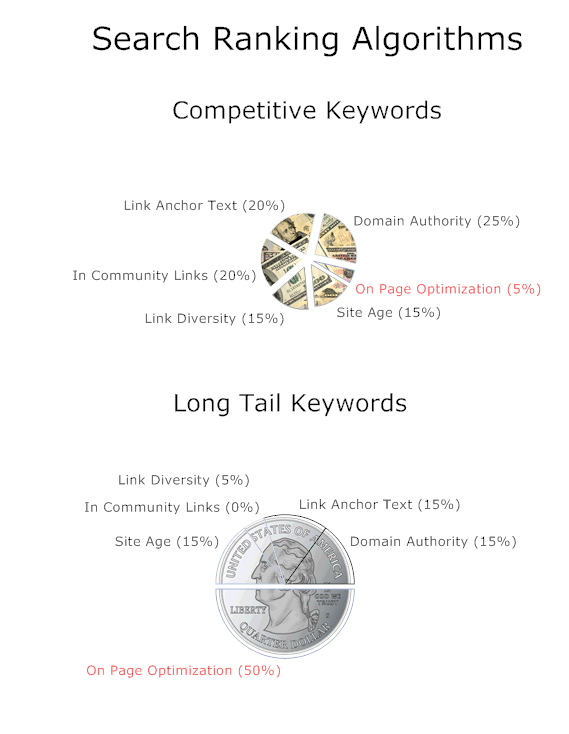
For really competitive queries links are crucial, but you can rank for many less competitive keywords and keyword variations without lots of links (because there is much less competition for those keywords). And even if you have lots of links, it is still typically hard to rank for keyword phrases that are not in your page copy.
Recommendations
With Google AdWords you can reach many of the stray searchers by using a combination of phrase match and broad match, and then using negative match to filter out irrelevant searches.
For every person searching for "seo" or "sem" there are probably 10 people searching for more obscure queries like "how do I promote my business on Google?" You can see how our page about link building ranks for hundreds of related keywords.
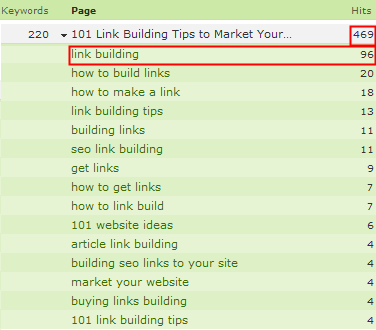
This is probably the single most powerful graphic explaination of why having lots of useful on-page content:

With SEO you can reach a lot of the searchers by using alternate word forms, alternate word orders, related phrases, and keyword modifiers in your content.
8. No Site Structure
Google AdWords
If your AdWords ad campaigns are not well organized then you are likely losing money. A strong site structure also helps ensure that your AdWords account has a strong structure, which can aid profitability.
SEO
If your site is not structured well then...
- navigation will likely be hard or confusing
- some of your key pages may not get much of your link authority
- some of your unimportant pages may accumulate a lot of your link authority
Recommendations
Most successful websites have a structure in which key pages which are mapped out against user demand and search volume.
- Create separate AdWords campaigns based on goals. Perhaps you can have campaigns for brand related searches, seasonal offers, public relations, campaigns that are based on ROI metrics, and even backfill campaigns like misspellings.
- Some content management systems (CMS) have major errors with duplicate content and site structure issues. A review of that topic is beyond the scope of this article, but search for the name of the CMS and SEO prior to implementing it to verify there are no serious issues and/or that there are easy fixes on the market.
- Set up site categories and sub-categories that are aligned against the keywords people use to search for your products and services.
- If you blog (or publish content regularly) reference older related materials when relevant.
- If your content is in a database you can use automated contextual links to help fix some site structural issues and redistribute PageRank down toward lower pages in your site structure.
9. Site With No Value Add
Google AdWords
If your site does not add much value it can be quite hard to sustain profit margins in the AdWords market. Affiliates routinely copy the work of each other and drive up click prices, which kills profit margins.
SEO
My very first profitable website was a no value add website that I got some spammy links for. The site did make thousands of dollars in affiliate commissions (a gift from God at the time), but that income was only made ***because*** I was a bad speller and misspelled some casino brand names back before search engines integrated spell correcting aggressivley. Such a site would simply go nowhere today.
Google often considers sites without value add to be unneeded duplication and/or spam. If you ever get a chance to read some of the Google Remote Quality Rater Documents you can see what Google believes is associated with "value add."
Recommendations
- In competitive AdWords markets competing businesses are forced to keep improving their business processes and efficiencies to be able to afford increasing bids from competing businesses.
- If you have a lower lifetime customer value than competing businesses you may eventually be driven out of the market.
- With some seedy affiliate offers in many cases the only people with sustained profit margins are basically those who are surprisingly sleazier than the rest of the market or those who are barely breaking even themselves, but are using their blog to build a downstream of followers that they get commissions from.
- Some (perhaps most?) affiliate networks ***will*** shave your commissions AND steal your keyword list if you send them the data.
- If you don't have a value add and want to play catch up in a competitive SEO market you need to have some sort of competitive advantage (be it nepotism, domain name, market experience, etc.).
- Making paid things freely available, creating useful software or tools, and having deeper & better editorial are 3 great ways to add value and win marketshare.
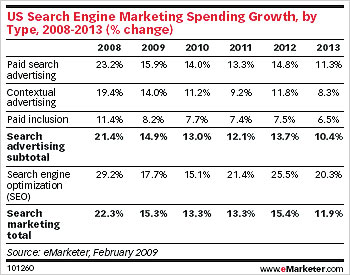
10. Competitive Saturated Market With Inadequate Budget
Google AdWords
In some markets it is hard to compete buying traffic without having a strong brand. If Geico pays Google $30 a click, but only pays affiliates $10 per lead then there is no way an affiliate can compete against Geico on the core industry keywords like auto insurance.
SEO
Want to rank for hotels and insurance? Me too. But I am uncertain if I have the resources to do it from scratch in a lasting manner given the algorithmic trends promoting well branded business and how corporations are increasing their SEO budgets.
Recommendations
- Have big ideas, but set reasonable goals, and measure progress.
- Do the math in advanced to estimate how much you can afford to pay for a click.
- Pick and chose your spots in the Google AdWords market. If after you do significant testing and optimization a word is still losing money consider dropping it.
- Try to pick a market position you feel you can dominate. The #20 result for "insurance" produces traffic worth ~ $0. The #2 or #3 result for "pet insurance" yields much more.
- Make at least 1 incremental improvement to your web business everyday.
- Aggressively re-invest early profits into growing your website and building a moat.
11. Picking a Market for 1
Google AdWords & SEO
If there is no demand for an idea then it is quite hard to create demand through search engine marketing. Search engine marketing works best when it captures existing demand.
Recommendations
- Keyword research tools can give you estimates of search volume.
- Since AdWords is so much quicker and easier to test than building a full site and implementing an SEO campaign, you can use AdWords to test market demand and interest for an offer before spending money building and marketing a full website.
- It can be good to be out front of trends (as one of the easiest ways to win a market is to be the first person in it), but just as easily you can go after an established high money market with your own original spin or angle.
12. Pick a Market Which Does Not Monetize
Google AdWords
If similar competing business models have much higher visitor value you may have to change your business model to compete. Some low earning business models might simply be precluded from participating in the AdWords market in a meaningful way.
SEO
There is nothing wrong with building a site about a topic you are passionate about and interested in without knowing how well it will monetize, but if you are trying to build a business you should pick something with a high enough visitor value to create enough profit potential to make it worth the time and money investment.
Recommendations
If you are planning on participating in the AdWords market, but have a low margin business then you should look for ways to increase profit margins, customer order size, and lifetime customer value.
If you run an editorial site it can be a good idea to under-monetize off the start to build market momentum without people viewing you as a competitor, but it can be hard to bolt on a business model if you have spent a lot of time servicing the wrong market segments.
13. Over-Aggressive Monetization From Day 1
Google AdWords
If you are buying traffic there is no problem with trying to monetize it. But most website visitors will not convert.
SEO
Sell in line text links & have pop ups? Is ever other post an affiliate link? If so, why would anyone want to subscribe to an ad stream when there are many useful alternatives to look at?
Recommendations
- Since most website visitors will not convert to paying customers on the first visit, you should look to establish a relationship with them by giving them a free offer and/or some reason to come back to your website. You can see the offer we make at the bottom of our pages and on our join now page.
- Existing leading trusted sites that have built up a following benefit from cumulative advantage. If your site is brand new and driven by editorial content it is a good idea to give away more value than you capture. Under-monetize until you build enough market momentum to make your rankings stick even when you do monetize.
- Consider monetizing some areas of your site more aggressively while not monetizing other sectors of your site, but instead using them for public relations and link building.
14. What Other Common SEM Errors do You See?


