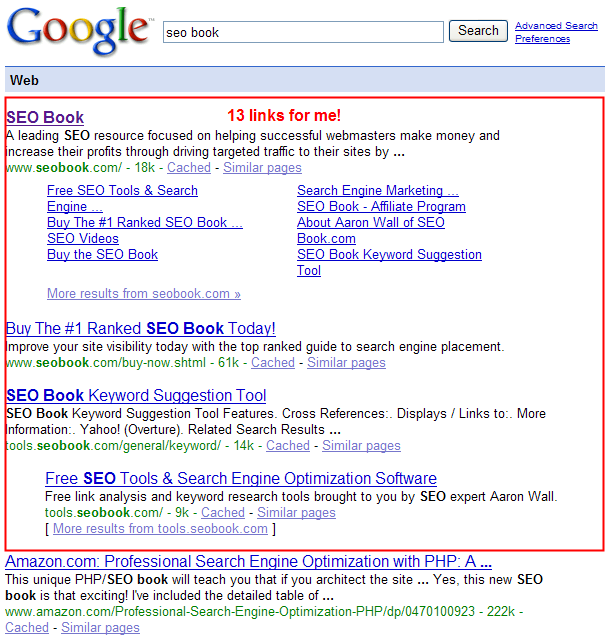
Google recently increased their number of sitelinks to 8 and now list them in a 2 column format. To visualize the value of this, consider that I have a decent sized monitor and only 1 listing not controlled by me appears above the fold when searching for SEO Book.
And look at a search for credit cards
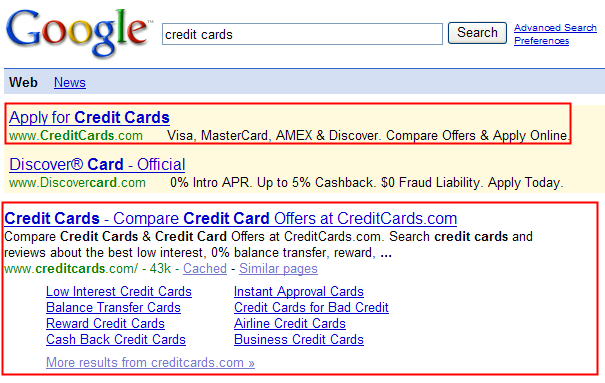
In time I have to expect that for high value keywords (as per AdWords advertiser stats) Google will manually review generic matching names with sitelinks to determine if they are brand oriented or not. If the sites with sitelinks for high value queries are not strong brand oriented sites, is Google going to keep giving this much exposure to whoever owns the exact match domain?
Using Organic Search Profits to Fund Ad Budgets that Lock Out Competing Sites
If the results stay like they are right now, Google is creating a dominate player that will likely overspend on the associated AdWords ads to further block out competition.
Who cares if you lose a few bucks on the ads if it further increases your volume to get you better payouts AND reinforces your default status as THE market leader? Plus, exact match domains consistently get a higher CTR than non-matching domains, so in that regard the domain name not only ensures the sitemap in the search results but also subsidizes the AdWords ad costs.
Domain Names Win Fatter Margins in the Game of Arbitrage
If, after seeing the above images, you still don't appreciate the value of domain names in search marketing, please give Frank Schilling's post on arbitrage titled The House Always Wins a read, then go on a domain buying binge.
Life isn't fair, but that doesn't mean that you should ignore the obvious deals! If you are a diverse publisher and domain names are not part of your SEO strategy, then hopefully you can correct that deficiency before the year is out.


