Google launched a new version of Google Trends which includes website traffic estimates, and highlights....
- visitor locations
- top keywords
- related sites
You need to be logged into a Google account to get a numerical scale on the traffic graph, but you can still get the general trend graphs and other data without logging in. Google also allows you to compare up to 5 sites at any given time
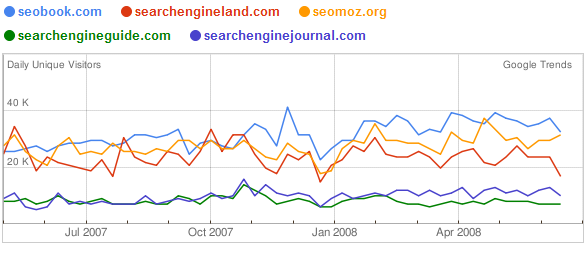
Search Engine Land reported that Google Trends...
This tool bases its data off Google search data, aggregated opt-in anonymous Google Analytics data, opt-in consumer panel data, and other third-party market research.
Those who wondered why using Google Analytics is a bad idea just got a taste of why it is a bad idea! Sure the data is only aggregated anonymously, but with Google owning 70% of the search market and having access to your analytics data you never know how deep they could decide to go through the data for competitive purposes. Is your site a keyword source for AdWords? How much of your data will appear on Google Trends?
You can't export the data yet and it only shows data for high traffic sites, but it is a great free tool for marketers.
- If sites do not show any data then they are probably either low traffic sites or penalized.
- The related sites feature lets you know how related your audience is to other sites, which is useful for determining how familiar their audience is or if you are reaching a new audience when buying ads.
- The top keywords shows you what competing sites are getting traffic from, and if those terms tend to be more brand oriented or more generic in nature...which is useful when thinking about the stability of a website you may want to purchase.
Fred Wilson did a review of Google Trends, comparing Google Analytics to Compete.com and comScore across 3 high traffic websites.
Since we are investors in these three companies and know what their internal numbers are saying, I can safely say that ComScore and Compete are lower but directionally correct. Google is like Alexa in that they don't report absolute numbers but even if they did, they are not directionally correct on this particular set of companies.
The fact that Google is even compared to the analytics firms with years of experience and algorithmic tuning shows how easily they could take a leading position in this market if they wanted it. Google will improve their accuracy, and at any point in time they could chose to expand the top 10 keywords to the top 100 or top 1,000.
The AP threatened to sue a blogger for quoting small passages, and at the same time the mainstream media is trying to redefine copyright for their own benefit. Eventually much of the mainstream media will start looking like eHow and Mahalo. Your content compiled and slightly rewritten by a third party. Your keyword list is their money list. Thousands of people are competing against you while you read this sentence. As your data leaks it is going to be tough to stay competitive unless you are often the topic of conversation. Public Relations is the only PR that matters.
I am probably a bit less pessimistic than Michael is at the moment, but firms are using G.P.S. data to create "reality mining" for offline analytics, predicting everything from traffic patterns, where to buy an ad, and where to place another store. A recent NYT article highlighted some such services:
Tony Jebara, also 34, the chief scientist and another co-founder of Sense, said, “We can predict tourism, we can tell you how confident consumers are, we can tell retailers about, say, their competitors, who’s coming in from particular neighborhoods.”
The idea of staying competitive through obscurity is obsolete. So you may as well be a loud mouth, encourage users to be loud mouths, and build a big brand that helps protect your plot from competitive market forces.


